Understanding CPC and CPM dives deep into the world of digital advertising metrics, shedding light on the nuances of Cost per Click and Cost per Mille. Get ready to explore the ins and outs of these essential concepts that drive online advertising strategies.
As we unravel the intricacies of CPC and CPM, you’ll gain valuable insights into how these metrics impact your ad campaigns and marketing efforts.
Understanding CPC and CPM
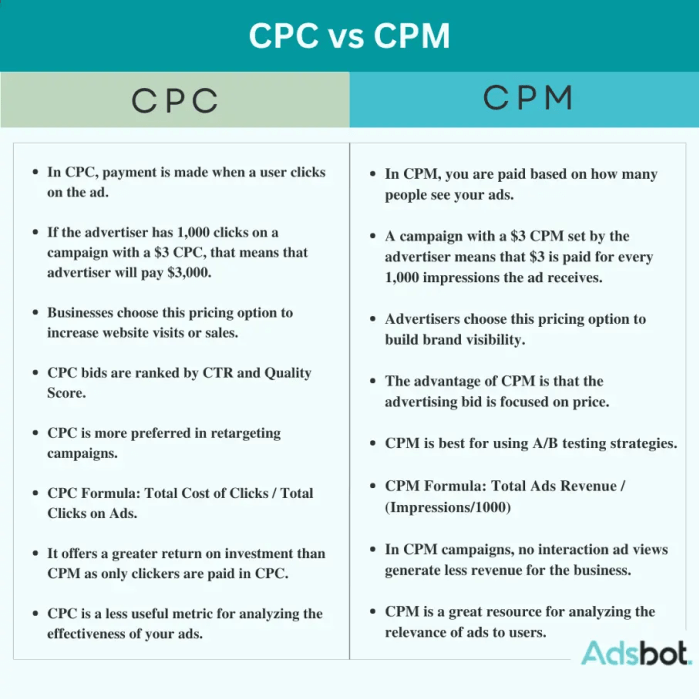
In the world of digital advertising, understanding key metrics like Cost per Click (CPC) and Cost per Mille (CPM) is crucial for creating successful campaigns.
Cost per Click (CPC)
Cost per Click (CPC) is a pricing model where advertisers pay a fee each time a user clicks on their ad. This means that advertisers only pay when their ad generates actual clicks, making it a performance-based metric.
- Example: An online shoe store uses CPC to track the effectiveness of their ads. They pay a set amount for each click their ad receives, regardless of how many times the ad is displayed.
Cost per Mille (CPM)
Cost per Mille (CPM), on the other hand, is a pricing model where advertisers pay for every 1,000 impressions of their ad. In this model, advertisers pay a set fee for a certain number of impressions, regardless of how many clicks the ad generates.
- Example: A beauty brand uses CPM to increase brand visibility. They pay a fixed amount for every 1,000 times their ad is displayed, regardless of how many clicks it receives.
When to Use CPC over CPM
In certain situations, using CPC might be more appropriate than CPM. This is especially true when the main goal of the campaign is to drive traffic to a website or increase conversions through clicks.
- Example: A new e-commerce site looking to drive sales might opt for CPC since they only pay when users click through to their site and potentially make a purchase. This ensures that they are directly paying for results.
Factors influencing CPC and CPM: Understanding CPC And CPM
In the world of digital advertising, several factors play a crucial role in determining the cost per click (CPC) and cost per thousand impressions (CPM) rates. Let’s delve into some of the key factors that influence these pricing models.
Industry and Competition Impact
The industry in which the ads are being placed and the level of competition within that industry can significantly impact CPC and CPM rates. Industries with high competition will generally have higher CPC and CPM costs as advertisers bid against each other to secure ad placements.
Ad Relevance and Quality Score Influence
Ad relevance and quality score are essential factors that affect CPC and CPM pricing. Search engines and advertising platforms reward ads that are relevant to the target audience with lower costs. Advertisers with high-quality ads that resonate with users can achieve lower CPC and CPM rates compared to those with lower-quality ads.
Targeting Options Impact, Understanding CPC and CPM
The targeting options chosen by advertisers can also influence CPC and CPM costs. Specific targeting parameters such as demographics, interests, and behaviors can help advertisers reach their desired audience more effectively. Advertisers willing to pay a premium for highly targeted placements may experience higher CPC and CPM rates but potentially see better results in terms of engagement and conversions.
Calculating CPC and CPM
In digital marketing, understanding how to calculate CPC (Cost Per Click) and CPM (Cost Per Mille) is crucial for optimizing advertising campaigns and maximizing ROI. Let’s break down the formulas and provide practical examples to illustrate these concepts.
Calculating CPC
To calculate CPC, you can use the following formula:
CPC = Total Cost of Campaign / Number of Clicks
For example, if you spent $100 on a campaign that generated 200 clicks, the CPC would be calculated as follows:
CPC = $100 / 200 clicks = $0.50 per click
Calculating CPM
CPM is calculated using the formula:
CPM = (Total Cost of Campaign / Impressions) x 1000
For instance, if you spent $500 on a campaign that received 100,000 impressions, the CPM would be calculated as:
CPM = ($500 / 100,000) x 1000 = $5 CPM
Advantages of Using CPC vs. CPM for Budgeting
- CPC allows advertisers to pay only when a user clicks on their ad, ensuring they are only charged for actual engagement.
- CPM can be beneficial for increasing brand awareness as advertisers pay for every 1,000 impressions, regardless of clicks.
- CPC is more performance-driven, as advertisers can directly measure the effectiveness of their ads based on the number of clicks received.
- CPM can be advantageous for campaigns focused on reach and visibility, where the goal is to maximize exposure to a broad audience.
- Choosing between CPC and CPM depends on campaign goals, budget constraints, and the desired outcome of the advertising efforts.
Optimizing CPC and CPM
When it comes to optimizing CPC and CPM, there are a few strategies you can implement to get the most out of your advertising campaigns and improve your ROI.
Optimizing CPC Campaigns
To optimize your CPC campaigns, focus on improving your ad relevance and quality score. Make sure your ads are highly targeted to the right audience and use relevant s to increase click-through rates.
- Regularly review and refine your list to eliminate irrelevant or underperforming s.
- Utilize ad extensions to provide additional information and encourage more clicks.
- Test different ad copies and landing pages to see which combination performs the best.
Improving CPM Rates and Ad Visibility
Improving your CPM rates and increasing ad visibility can help you reach a larger audience and maximize your ad exposure.
- Focus on creating eye-catching and engaging ad creatives to capture users’ attention.
- Utilize targeting options to reach the right audience at the right time.
- Experiment with different ad formats and placements to see which ones generate the most impressions.
A/B Testing for Pricing Model Optimization
A/B testing can help you determine the most effective pricing model between CPC and CPM for your advertising campaigns.
- Run parallel campaigns with the same ad creative but different pricing models to compare performance.
- Track key metrics such as click-through rates, conversion rates, and overall ROI to evaluate the effectiveness of each pricing model.
- Adjust your budgets and bids based on the results of your A/B tests to optimize your campaigns for maximum results.